AWS Machine Learning Blog
Category: AWS Trainium
PEFT fine tuning of Llama 3 on SageMaker HyperPod with AWS Trainium
In this blog post, we showcase how you can perform efficient supervised fine tuning for a Meta Llama 3 model using PEFT on AWS Trainium with SageMaker HyperPod. We use HuggingFace’s Optimum-Neuron software development kit (SDK) to apply LoRA to fine-tuning jobs, and use SageMaker HyperPod as the primary compute cluster to perform distributed training on Trainium. Using LoRA supervised fine-tuning for Meta Llama 3 models, you can further reduce your cost to fine tune models by up to 50% and reduce the training time by 70%.
Serving LLMs using vLLM and Amazon EC2 instances with AWS AI chips
The use of large language models (LLMs) and generative AI has exploded over the last year. With the release of powerful publicly available foundation models, tools for training, fine tuning and hosting your own LLM have also become democratized. Using vLLM on AWS Trainium and Inferentia makes it possible to host LLMs for high performance […]
Enhanced observability for AWS Trainium and AWS Inferentia with Datadog
This post walks you through Datadog’s new integration with AWS Neuron, which helps you monitor your AWS Trainium and AWS Inferentia instances by providing deep observability into resource utilization, model execution performance, latency, and real-time infrastructure health, enabling you to optimize machine learning (ML) workloads and achieve high-performance at scale.
Deploy Meta Llama 3.1 models cost-effectively in Amazon SageMaker JumpStart with AWS Inferentia and AWS Trainium
We’re excited to announce the availability of Meta Llama 3.1 8B and 70B inference support on AWS Trainium and AWS Inferentia instances in Amazon SageMaker JumpStart. Trainium and Inferentia, enabled by the AWS Neuron software development kit (SDK), offer high performance and lower the cost of deploying Meta Llama 3.1 by up to 50%. In this post, we demonstrate how to deploy Meta Llama 3.1 on Trainium and Inferentia instances in SageMaker JumpStart.
Scaling Rufus, the Amazon generative AI-powered conversational shopping assistant with over 80,000 AWS Inferentia and AWS Trainium chips, for Prime Day
In this post, we dive into the Rufus inference deployment using AWS chips and how this enabled one of the most demanding events of the year—Amazon Prime Day.
Node problem detection and recovery for AWS Neuron nodes within Amazon EKS clusters
In the post, we introduce the AWS Neuron node problem detector and recovery DaemonSet for AWS Trainium and AWS Inferentia on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS). This component can quickly detect rare occurrences of issues when Neuron devices fail by tailing monitoring logs. It marks the worker nodes in a defective Neuron device as unhealthy, and promptly replaces them with new worker nodes. By accelerating the speed of issue detection and remediation, it increases the reliability of your ML training and reduces the wasted time and cost due to hardware failure.
AWS AI chips deliver high performance and low cost for Llama 3.1 models on AWS
Today, we are excited to announce AWS Trainium and AWS Inferentia support for fine-tuning and inference of the Llama 3.1 models. The Llama 3.1 family of multilingual large language models (LLMs) is a collection of pre-trained and instruction tuned generative models in 8B, 70B, and 405B sizes. In a previous post, we covered how to deploy Llama 3 models on AWS Trainium and Inferentia based instances in Amazon SageMaker JumpStart. In this post, we outline how to get started with fine-tuning and deploying the Llama 3.1 family of models on AWS AI chips, to realize their price-performance benefits.
The future of productivity agents with NinjaTech AI and AWS Trainium
NinjaTech AI’s mission is to make everyone more productive by taking care of time-consuming complex tasks with fast and affordable artificial intelligence (AI) agents. We recently launched MyNinja.ai, one of the world’s first multi-agent personal AI assistants, to drive towards our mission. MyNinja.ai is built from the ground up using specialized agents that are capable of completing tasks on your behalf, including scheduling meetings, conducting deep research from the web, generating code, and helping with writing. These agents can break down complicated, multi-step tasks into branched solutions, and are capable of evaluating the generated solutions dynamically while continually learning from past experiences. All of these tasks are accomplished in a fully autonomous and asynchronous manner, freeing you up to continue your day while Ninja works on these tasks in the background, and engaging when your input is required.
Scale and simplify ML workload monitoring on Amazon EKS with AWS Neuron Monitor container
Amazon Web Services is excited to announce the launch of the AWS Neuron Monitor container, an innovative tool designed to enhance the monitoring capabilities of AWS Inferentia and AWS Trainium chips on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS). This solution simplifies the integration of advanced monitoring tools such as Prometheus and Grafana, enabling you to […]
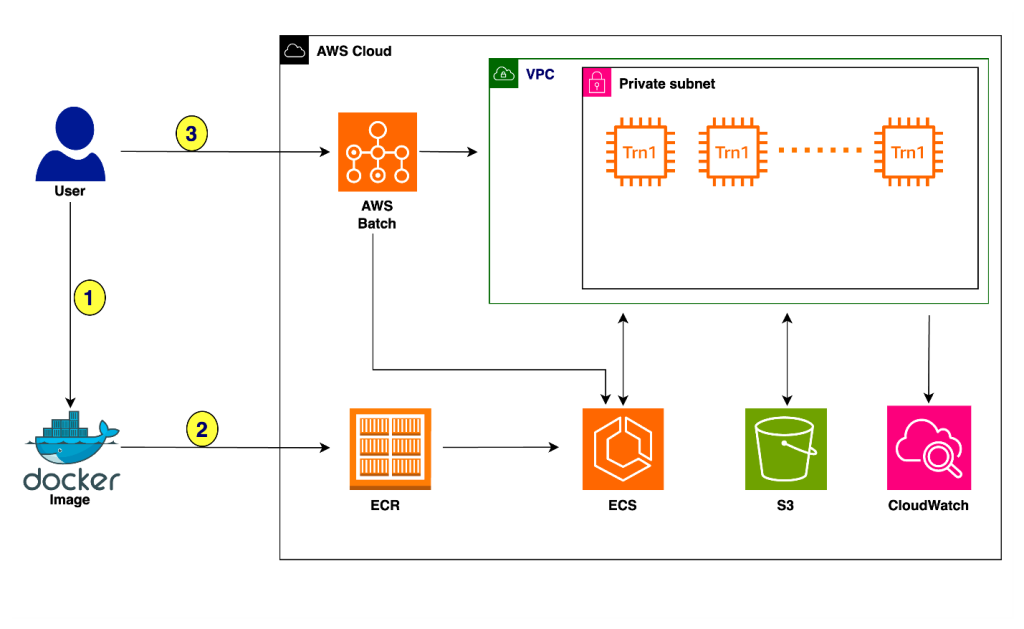
Accelerate deep learning training and simplify orchestration with AWS Trainium and AWS Batch
In large language model (LLM) training, effective orchestration and compute resource management poses a significant challenge. Automation of resource provisioning, scaling, and workflow management is vital for optimizing resource usage and streamlining complex workflows, thereby achieving efficient deep learning training processes. Simplified orchestration enables researchers and practitioners to focus more on model experimentation, hyperparameter tuning, […]