Clinical Risk Management is all about keeping patients safe and providing top-notch care. This guide breaks down the important steps and strategies. Whether you're new to healthcare or have years of experience, it's here to help you understand and handle risks in the best way possible.
In this article
Part 1: What is Risk Management?
Risk management is like being a careful planner. It's about looking ahead and preparing for things that might go wrong. In different areas like business or healthcare, it means making smart choices to prevent problems and keep things safe and on track.
In everyday life, we use risk management when we look both ways before crossing the street. It's about being cautious and making decisions that protect us from harm. Similarly, in businesses and industries, it helps them run smoothly and avoid unexpected troubles.
Part 2: Understanding What is Clinical Risk?

Clinical risk management refers to the potential for harm or adverse events occurring within a healthcare setting. It encompasses a wide range of situations, from medication errors to surgical complications. Identifying and managing clinical risks is crucial for ensuring patient safety and quality of care. This involves thorough assessment, prevention, and effective response strategies to minimize the likelihood of harm and provide the best possible outcomes for patients.
Part 3: Importance Of Clinical Risk Assessment In Healthcare Industry
Clinical risk assessment plays a pivotal role in the healthcare industry for a variety of reasons:
- Enhances Patient Safety: Identifying potential risks allows for proactive measures to be taken, reducing the likelihood of patient harm.
- Improves Quality of Care: Effective risk assessment leads to better decision-making, ensuring patients receive the highest standard of healthcare.
- Regulatory Compliance: It helps healthcare facilities meet industry standards and legal requirements, safeguarding against potential liabilities.
- Enhances Reputation: Demonstrates a commitment to patient safety, building trust and confidence in the healthcare provider.
- Cost Savings: Prevents costly legal actions and medical interventions associated with adverse events.
Part 4: Create a Clinical Risk Management Diagram Easily Using EdrawMax
EdrawMax revolutionizes clinical risk assessment by offering a user-friendly platform for creating informative and visually engaging diagrams. With its intuitive interface, healthcare professionals can efficiently translate complex risk scenarios into clear visual representations. The extensive library of customizable templates further expedites the process, allowing for tailored risk assessments. This tool not only enhances communication within healthcare teams but also facilitates well-informed decision-making.
Moreover, by utilizing EdrawMax, healthcare organizations can ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, ultimately fostering a safer and more secure patient care environment.
Here are the steps to create a clinical risk management diagram using EdrawMax in just a few clicks:
Step1
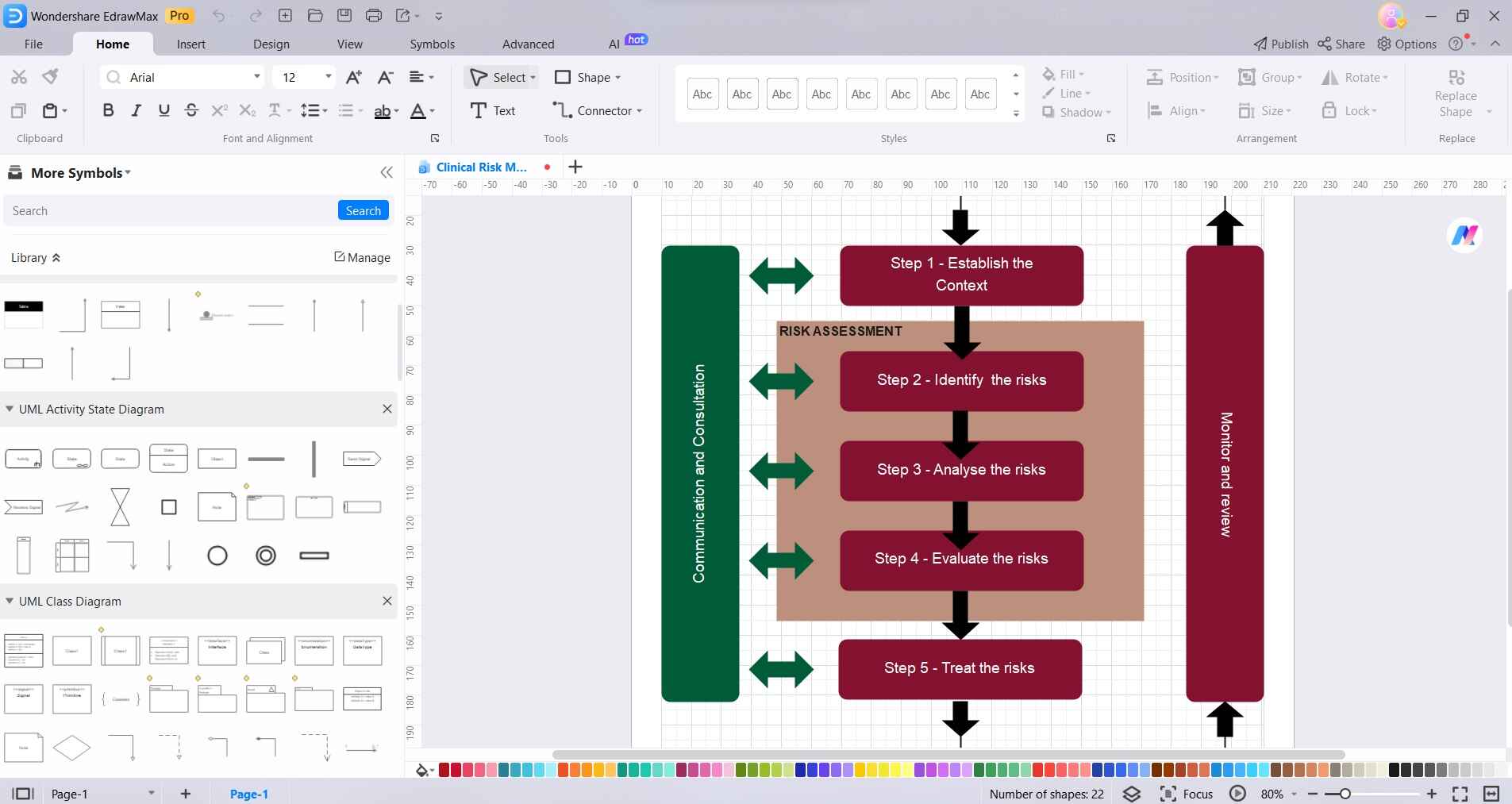
Open EdrawMax on your computer or device. Switch to the ŌĆ£TemplateŌĆä1ż7 section from the left menu pane. Choose a clinical risk management template from the extensive library provided. Hit on the ŌĆ£Use ImmediatelyŌĆä1ż7 button to export it to the canvas.

Step2
Add, delete, or modify elements to fit your specific risk assessment scenario.

Step3
Clearly label each component of the diagram and arrange them logically. Use the left sidebar to add connectors and 3D objects in the diagram, if required. Include relevant details or descriptions to enhance clarity.
Step4
Click on any entity and select ŌĆ£StylesŌĆä1ż7. Customize the appearance of the diagram using EdrawMax's theme and style options.

Step5
Head to File> Save to save the diagram. Double-check for accuracy and completeness before saving or exporting your diagram.
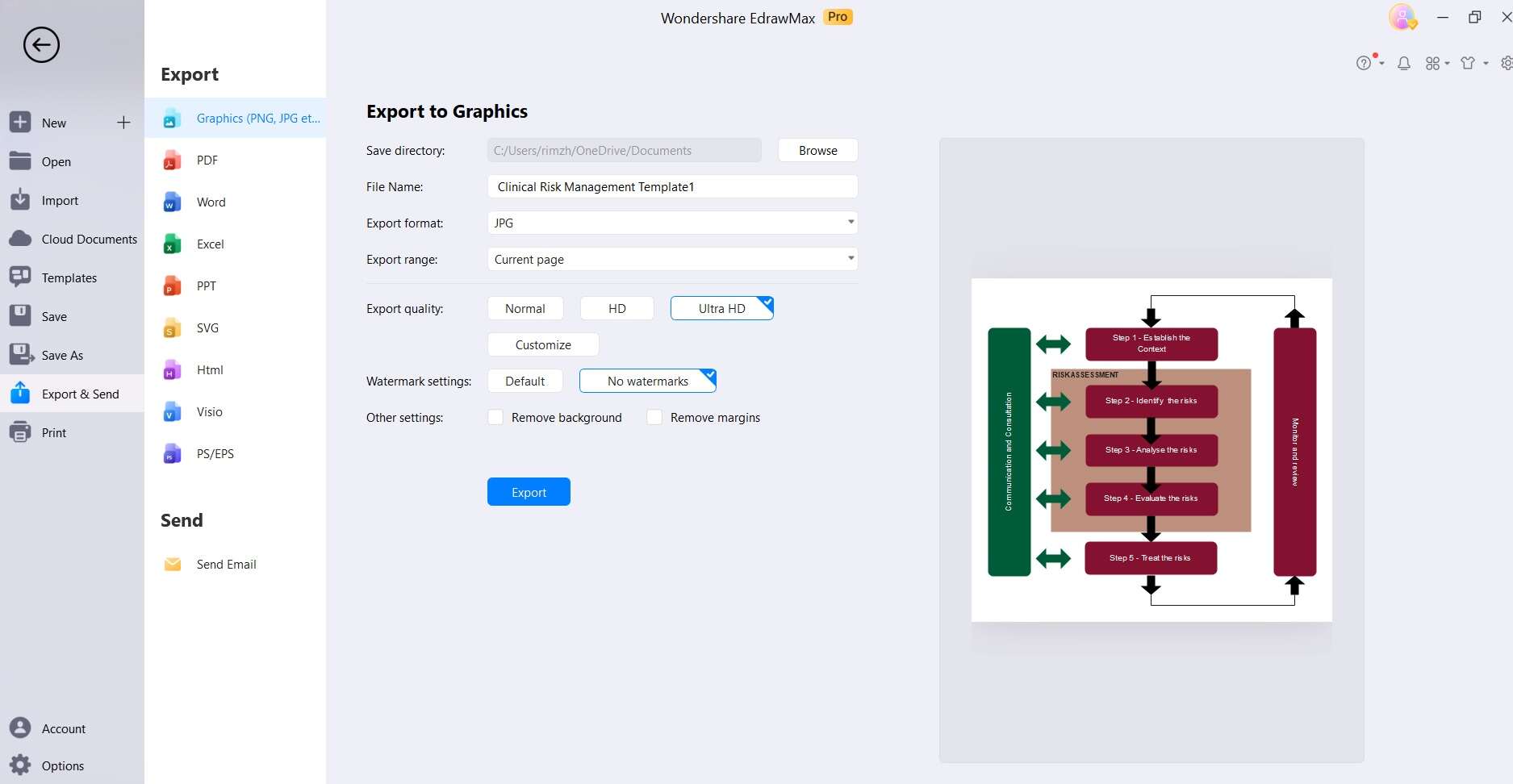
With EdrawMax, creating a clinical risk management diagram is a breeze, allowing you to focus more on proactive problem-solving and ensuring patient safety in healthcare. Start streamlining your risk assessment processes today!
Part 5: Role of a Clinical Risk Manager
A Clinical Risk Manager plays a vital role in healthcare by identifying and assessing potential risks to patient safety. They develop and implement strategies to mitigate these risks, ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, they provide training to staff, respond to incidents, and conduct thorough analyses for continuous improvement.
By maintaining meticulous documentation and collaborating with healthcare teams, they contribute to a culture of patient safety and quality care. Their advocacy for best practices and proactive problem-solving is instrumental in creating a secure healthcare environment.
Part 6: Tips for Proactive Clinical Risk Management
Proactive clinical risk management is crucial for maintaining patient safety and quality care in healthcare settings. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your approach:
- Regular Training: Ensure staff are well-versed in risk identification and mitigation strategies.
- Robust Documentation: Maintain detailed records of incidents, assessments, and implemented measures.
- Constant Communication: Foster an open dialogue among healthcare teams to promptly address emerging risks.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with industry trends, regulations, and best practices in clinical risk management.
- Root Cause Analysis: Thoroughly investigate incidents to understand underlying causes and implement targeted solutions.
- Regular Audits: Conduct routine assessments to identify potential risks and verify the effectiveness of existing measures.
- Patient Engagement: Involve patients in their care plans, ensuring their concerns and preferences are considered in risk assessments.
Conclusion
In summary, being proactive about clinical risk management is crucial for keeping patients safe and providing top-notch care. By training staff, keeping good records, and talking openly, healthcare providers can catch and handle potential problems early. Staying updated and involving patients in their care are also key. These steps create a safer healthcare environment and lead to better results for patients, building trust in the healthcare system.