Binding an EIP to the Extended Network Interface of an ECS to Enable Internet Access
Scenarios
As shown in Figure 1, the ECS has two network interfaces, one primary network interface and one extended network interface. You can bind an EIP to the extended network interface of the ECS and configure policy-based routes to ensure that the ECS can access the Internet through the EIP.
This section uses a Linux ECS as an example.
Step 1: Create Cloud Resources and Attach an Extended Network Interface
- Create a VPC and two subnets in the VPC.
In this example, the primary and extended network interfaces of the ECS are in different subnets.
For details, see Creating a VPC and Subnet.
- Create an ECS in the VPC subnet.
For details, see Purchasing a Custom ECS.
- Create a network interface and attach it to the ECS as an extended network interface.
When creating a network interface, select a different subnet from where the primary network interface is created. For details, see Creating a Network Interface.
Attach the network interface to the ECS. For details, see Attaching a Network Interface to a Cloud Server.
- Assign an EIP and bind it to the extended network interface of the ECS.
For details, see Assigning an EIP.
Bind the EIP to the extended network interface of the ECS. For details, see Binding an EIP to a Network Interface.
Step 2: Obtain the ECS Network Information
- Obtain the private IP addresses of the ECS's network interfaces.
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
- Obtain the gateway address of the subnet.
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
- Click Service List and choose Compute > Elastic Cloud Server.
- In the ECS list, locate the target ECS and click its name.
- In the ECS Information area, click the VPC name.
The Virtual Private Cloud page is displayed.
- In the VPC list and click the number in the Subnets column.
The Subnets page is displayed.
- In the subnet list, click the subnet name.
- In the Gateway and DNS Information area, view the gateway address of the subnet.
Figure 2 Viewing the gateway address of the subnet

Step 3: Configure Policy-based Routes for the Extended Network Interface
- ECS Remotely log in to the ECS.
For details, see How Do I Log In to My ECS?
- Run the following command to query the route information of the network interface:
The following figure is displayed. In this figure:
- The destination of the route for the primary network interface is 192.168.11.0/24.
- The destination of the route for the extended network interface is 192.168.17.0/24.

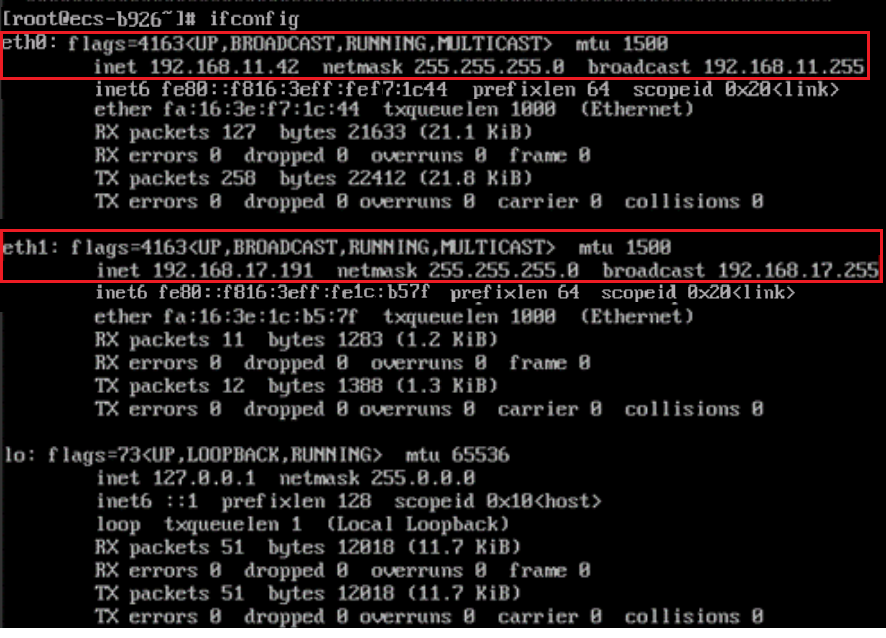
- Run the following command to query the network interface names of the ECS:
The following figure is displayed. Search for the network interface name based on the network interface address. In this figure:
- 192.168.11.42 is the IP address of the primary network interface, and the network interface name is eth0.
- 192.168.17.191 is the IP address of the extended network interface, and the network interface name is eth1.
- Configure the default route for the ECS so that it can access the Internet through the extended network interface.
- Run the following command to delete the default route of the primary network interface:
route del -net 0.0.0.0 gw <subnet-gateway-IP-address> dev <network interface-name>
The parameters are described as follows:
- 0.0.0.0: destination IP address, indicating that multiple IP addresses are matched. Do not change the value.
- Subnet gateway IP address: Enter the subnet gateway address of the primary network interface collected in section Table 1.
- Network interface name: Enter the name of the primary network interface obtained in 3.
Example command:
route del -net 0.0.0.0 gw 192.168.11.1 dev eth0
This operation will interrupt ECS traffic.
- Run the following command to configure the default route for the extended network interface:
route add default gw Subnet-gateway-IP-address
The parameters are described as follows:
Subnet gateway IP address: Enter the subnet gateway address of the extended network interface collected in section Table 1.
Example command:
route add default gw 192.168.17.1
- Run the following command to delete the default route of the primary network interface:
- Verify network connectivity.
Run the following command to check whether the ECS can access the Internet:
ping Public-IP-address-or-domain-name
Example command:
ping support.huaweicloud.com
If information similar to the following is displayed, the ECS can communicate with the Internet.[root@ecs-a01 ~]# ping support.huaweicloud.com PING hcdnw.cbg-notzj.c.cdnhwc2.com (203.193.226.103) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 203.193.226.103 (203.193.226.103): icmp_seq=1 ttl=51 time=2.17 ms 64 bytes from 203.193.226.103 (203.193.226.103): icmp_seq=2 ttl=51 time=2.13 ms 64 bytes from 203.193.226.103 (203.193.226.103): icmp_seq=3 ttl=51 time=2.10 ms 64 bytes from 203.193.226.103 (203.193.226.103): icmp_seq=4 ttl=51 time=2.09 ms ... --- hcdnw.cbg-notzj.c.cdnhwc2.com ping statistics --- 4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 3004ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 2.092/2.119/2.165/0.063 ms
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






