
Agile Business, agile security: How AI and Zero Trust work together
Traditional security approaches don’t work for AI. Generative AI technology is already transforming our world and has immense positive potential for cybersecurity and business processes, but traditional security models and controls aren’t enough to manage the security risks associated with this new technology.
We recently published a new whitepaper that examines the security challenges and opportunities from generative AI, what security must do to adapt to manage risk related to it, how a Zero Trust approach is essential to effectively secure this AI technology (and underlying data), and how different roles across your organization must work together for effective AI security.

Navigating AI’s unique challenges
AI presents new types of problems that require different thinking and different solutions.
Generative AI is dynamic
At the most fundamental level, generative AI is non-deterministic computing, which means that it doesn’t provide the exact same output each time you run it. For example, asking an image generation model to “draw a picture of a kitten in a security guard uniform” repeatedly is unlikely to generate the exact same picture twice (though they will all be similar). Static security controls assume that vulnerabilities (in the broader definition) and their exploitation so they will look exactly the same each time will not be particularly effective at detecting and blocking attacks on AI. You need controls made for AI.
Generative AI is data-centric
Generative AI is fundamentally a data analysis and data generation technology, making the security and governance of your data incredibly important to the security of your AI applications and the reliability and trustworthiness of their outputs.
You need to have an asset-centric and data-centric security approach that can handle dynamic changes to secure AI and the data it relies on. This means you need a Zero Trust approach to effectively secure AI.
Zero Trust is simply modern security without the false assumption that a network security perimeter is enough to secure assets in it (including data). This drives a mindset shift that changes how you look at security strategy, architecture, controls, and more. Zero Trust focuses security protecting business assets inside and outside the classic network perimeter across the ‘hybrid of everything’ environments (including multiplatform, multicloud, on-premises, operational technology, Internet of Things, and more).
Cyberattackers are using generative AI against you
Another complication is that AI relies on vast amounts of data to train models, making your data a prime target for cyberattackers and elevating the importance of protecting your data. Cybercriminals are also using AI now to refine attack techniques and process the data they steal from organizations. Organizations must recognize that these threats are already happening and urgently adapt their security strategies to effectively protect their data, AI applications, business assets, and people.
By applying Zero Trust principles, organizations can reduce the risk related to AI while rapidly embracing the opportunities that this technology offers.
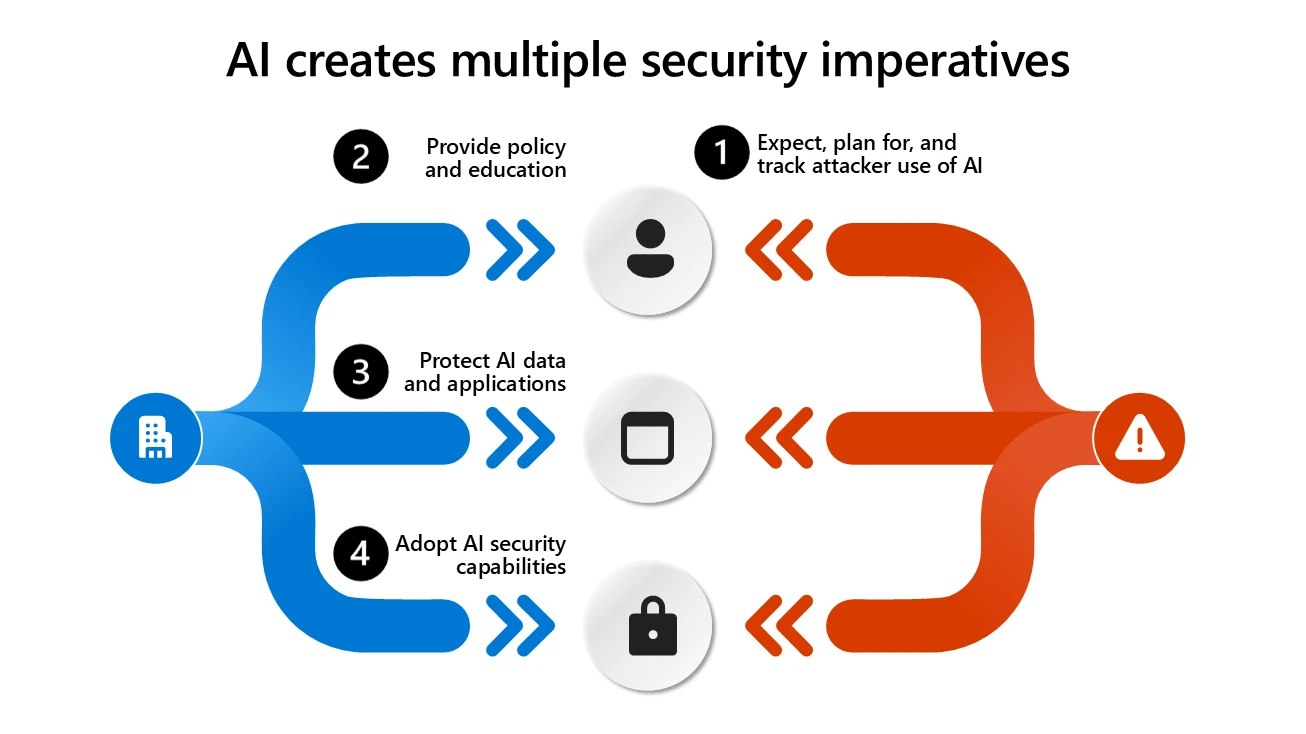
Key strategies to help manage AI security risks
These strategies from the whitepaper illustrate how to manage the risks associated with AI.
- Provide guidance to users. Cyberattackers are using AI to improve the quality and volume of scam emails and phone calls (sometimes called phishing or business email compromise) that will be experienced by nearly anyone in the organization. Organizations must urgently start educating everyone (starting with financial roles and other high-business-impacting roles) so that they understand that they are likely to see these highly convincing fake communications and what to do about it. People will need to understand the basics of how AI works, the risks that it poses, and what they can do about it (such as how to spot it, how to report it to security teams, or how to enhance business processes to independently verify important transactions).
- Protect AI applications and data. Cybercriminals are actively targeting AI systems. Early integration of security in AI development is crucial to avoid costly fixes later.
- Adopt AI security capabilities. While AI is not a magical silver bullet that can replace talented human experts and existing tools, AI technology can significantly enhance security operations (SecOps) by empowering people to get more out of their data and tools (quickly writing up reports, analyzing business impact of attacks, guiding newer analysts through investigation, and more).
- Policy and standards. Organizations need written security standards and processes to guide their team’s decisions and demonstrate they are following due diligence to regulators. These standards should cover security, privacy, and ethical considerations—you can use Microsoft’s Responsible AI Standard as a reference to guide this work.
Zero Trust and AI: A symbiotic relationship
We have found that there is a symbiotic relationship between Zero Trust and Generative AI where:
- AI requires a Zero Trust approach to effectively protect data and AI applications.
- AI-powered capabilities can help accelerate Zero Trust by analyzing vast data signals, extracting key insights, guiding humans through key processes, and automating repetitive manual tasks. This allows your teams to cut through the noise, responding to threats faster, and continuously learn and grow their expertise.
The Zero Trust approach to security helps you keep up with continuously changing threats as well as the rapid evolution of technology that AI represents. I will wrap this blog with a quote from the new whitepaper:
“By integrating security early and embracing Zero Trust principles, organizations can take advantage of AI while mitigating risks, much like brakes on a car enable people to safely travel faster.”
Learn more about the Zero Trust approach
To learn more about how Zero Trust can guide this approach, visit the Zero Trust Model webpage and explore additional resources at the Zero Trust Guidance Center. Check out Mark’s List for additional resources.
For more security resources and links, you can visit our LinkedIn. You can also bookmark the Security blog to keep up with security news and follow Microsoft Security on LinkedIn and X (@MSFTSecurity).

