How to Choose Binoculars: Table of Contents
General Use Binoculars - Hiking, Stadium Sports, Outdoor ![]()
Behind the Numbers and Terminology
What Types of Binoculars Are There?
 TRYBE Defense Binoculars
TRYBE Defense BinocularsBinoculars are the world's most used optical instrument, other than eyeglasses, and they have a lot of different uses. Choosing the best binoculars for your specific application can be a challenge and this guide is intended to help you understand binoculars better. Consider when, where, and how often you plan to use the binocular to select the right combination of features that are right for your needs.
General Use Binoculars - Hiking, Stadium Sports, Outdoor
Compact and wide-angle binoculars are great for outdoor activities and getting closer to the action watching sporting events at the stadium.Compact binoculars are usually found at 7x25 to 10x50 ranges. Compact binoculars are easy to store in your pocket or on a strap around your neck and the wide-angle presents a good field of view.
Hunting Binoculars
7x18 to 10x56 binoculars are best for hunting applications. For long-range shooting, such as varmint hunting, more powerful binoculars like 12x40 to 16x50 are best. At larger magnification, you will need to use a tripod to stabilize the binoculars, as the image will be very shaky if used in a standing position. The shaking of your hands is amplified by the larger magnification.
Bird Watching
The standard binocular for birding is an 8x42 binocular. To see more details on smaller birds at greater distances, you may opt for a 10x42 to a 12x50. Longer eye relief and a close focus are also great features to have on your bird-watching binoculars.
Boating and Marine Binoculars
Since you're on the water, a high magnification binocular is not advised. The most commonly used magnifications are 7x40 to 7x50, but 8x40 to 10x50 are also chosen by some mariners and boating enthusiasts. A larger objective lens, waterproof, and rubber armor are the main features to look for in a marine and boating binocular.
Concert/Theater Binoculars
Compact binoculars with a wide-angle are great for concert and theater viewing using a binocular. 3x25, 4x30, 5x25, 7x18, 7x21, and 8x25, are great for venues such as opera, theater, and music concerts.
Behind the Numbers and Terminology

| Terminology | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1: | Diopter Adjustment | |
| 2: | Ocular Lens Assembly | |
| 3: | Prism System | |
| 4: | Focus System | |
| 5: | Hinge | |
| 6: | Objective Lens | |
Binoculars are often referred to as two numbers separated with an "x". For example, 8x32. The first number is the power or magnification of the binocular. With an 8x32 binocular, the object being viewed appears to be eight times closer than you would see it with the unaided eye. We do NOT recommend using binoculars with magnification over 10x without a tripod - if you go with too much magnification in a hand-held binocular, your image will be very shaky! Also, many people ask, "How far can you see with a binocular?" We always answer, "You can see as far your eyes can see, but the objects will seem to be closer, magnified by the power of your binoculars."
 The second number in the formula (8x32) is the diameter of the objective or front lens in millimeters. The larger the objective lens, the more light that enters the binocular, and the brighter the image.
The second number in the formula (8x32) is the diameter of the objective or front lens in millimeters. The larger the objective lens, the more light that enters the binocular, and the brighter the image.
One of the numbers you will see in a specification table for binoculars is an exit pupil. This refers to the size of the circle of light visible at the eyepiece of a binocular. The larger the exit pupil, the brighter the image. To determine the size, divide the objective lens diameter by the power. For example, an 8x32 model has an exit pupil of 4mm (32÷8=4).
Exit pupil is a very rough guide to image brightness. Binoculars with large exit pupils provide brighter images under very low light conditions. For normal daylight viewing, an exit pupil of 2.5mm or 3mm is fine. For astronomy, an exit pupil of 5-7mm is preferred. An exit pupil larger than 7mm is a waste of light since the human eye cannot open wide enough to accept an exit pupil larger than this. Exit pupil should not be taken too literally since it treats all binoculars, regardless of lens coatings and optical quality, as if they are the same.
When talking about binoculars, you may hear the term "light transmission" thrown around. This refers to the efficiency of an optic, or its ability to deliver the maximum amount of the light entering the objective lens to the eye.
- Relative brightness, like exit pupil, is a rough guide to image brightness. It is simply an exit pupil squared, so a binocular with an exit pupil of 5mm will have a relative brightness of 25. As with exit pupil, relative brightness should not be taken too literally, since it treats all binoculars, regardless of lens coatings and optical quality as if they are the same. In actual tests, some premium-grade compacts with a low relative brightness are brighter than some full-size binoculars.
- Twilight factor is a mathematical formula that predicts the amount of detail that can be seen in low light. The twilight factor is the square root of magnification times objective. A 10x40 will have a twilight factor of 20 (square root of 10x40). As with exit pupil and relative brightness, the twilight factor should not be taken too literally, since it treats all binoculars, regardless of lens coatings and optical quality as if they are the same. No $50 binocular will ever equal a premium-grade binocular for low-light detail, even though they both have the same exit pupil.
- Eye relief is the distance a binocular can be held away from the eye and still present the full field of view. Extended or long eye relief reduces eyestrain and is ideal for eyeglass wearers. Binoculars come with Twist-Up, Pop-Up, or soft rubber Fold-Down eyecups which go down for eyeglass wearers. These options allow everyone to see the entire field of view.
- Those that don't always wear eyeglasses, but don't have 20/20 vision or have different vision in each eye, can use diopter adjustment. This is a fine focus adjustment usually provided around one eyepiece to accommodate for vision differences between the right and left eyes.
- Field of View (FOV) is the side-to-side measurement of the circular viewing field or subject area. It is defined by the width of the area visible at 1000 yards or meters. A wide-angle binocular features a wide field of view and is better for following action. The field of view is determined by two things. The first is magnification. In general, as magnification goes up, the field of view goes down. A 10x42 will show more detail in that fence at 1,000 yards than an 8x42, but it will not show you as wide a section of fence. The second thing that determines the field of view in a binocular is the eyepiece design. Wide-angle design eyepieces of good optical quality, however, are expensive. Inexpensive binoculars with wide-angle eyepieces are usually not as sharp as standard binoculars.
- Most binoculars have a focus knob, and the specifications of the model will list a "minimum focus" or "close focus". This is the nearest distance at which a binocular will focus on an object. A binocular will not focus on an object closer than this distance. This feature is important for some applications such as birding.
- Another number you may see when looking at binoculars is the inter-pupillary distance or IPD. It is the distance between the eyes that differs from person to person. The adjustment for this difference is accomplished by opening or closing the hinged portion of the binocular to bring the eyepieces closer together or farther apart.
What Types of Binoculars Are There?
Binocular come in two different prism systems - Porro and Roof prism. In Porro prism binoculars the objective or front lens is offset from the eyepiece. Porro prism binoculars provide greater depth perception and generally offer a wider field of view. In roof prism binoculars the prisms overlap closely, allowing the objective lenses to line up directly with the eyepiece. The result is a slim, streamlined shape in which the lenses and prisms are in a straight line. Most optical prisms are made from borosilicate (BK-7) glass or barium crown (BAK-4) glass. BAK-4 is the higher-quality glass yielding brighter images and high edge sharpness.
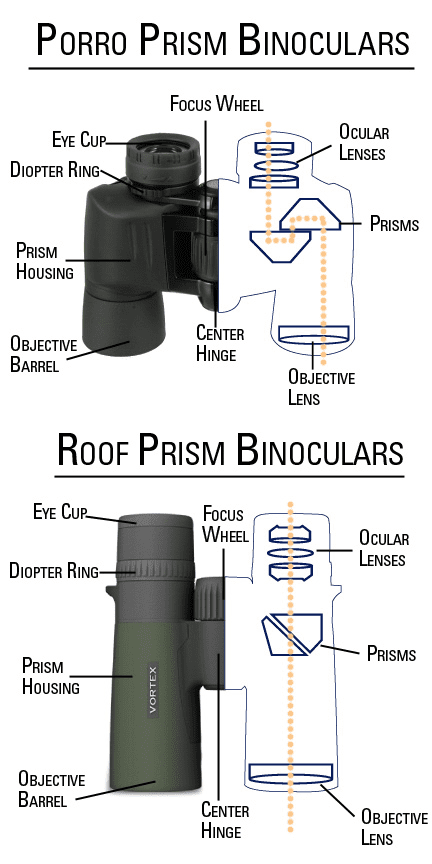 Porro vs. Roof Prism Binoculars Diagram
Porro vs. Roof Prism Binoculars Diagram- Standard Size Binoculars - A standard or full-size binocular can be used for everything from nature observation to spectator sports.
- Compact Binoculars - Smaller and lighter in weight and are a good choice to take along to the theater or concerts or on hikes and hunting trips.
- Wide-Angle Binoculars - Ideal for tracking fast-moving action across wide areas such as football fields, racetracks, and wilderness terrain.
- Zoom Binoculars - A zoom binocular allows the user to increase the magnification to focus in on the details. From distant to near views, it's the best of both worlds.
- Waterproof Binoculars - Waterproof binoculars deliver clarity despite foul weather conditions including fog, rain, and ice. O-ring sealed and nitrogen purged for reliable fog-proof, waterproof performance.
- Center Focus Binocular - This type of binocular uses a single wheel to focus on objects. It can focus on objects both very close and far away, making it the most versatile and commonly used focusing system on a binocular.
- Individual Eyepiece Focus Binoculars - An individual eyepiece focus binocular requires you to focus each eyepiece when looking at an object, but once focused for your eyes, objects from 40 yards away to infinity are always in focus and require no additional focusing. This is a great system for medium-range and long-range objects, but it is not well suited for close-in work. IF binoculars are most commonly found in marine binoculars and astronomy binoculars.
- No Focus, or Focus-Free Binoculars - This is an economy version of an individual eyepiece focus binocular, but the eyepieces are locked and set at the factory and cannot be adjusted. This means that you can never focus on objects closer than forty yards away and it also means that the binocular cannot be adjusted for differences in strength between your right eye and left eye. This is a serious shortcoming for most people since most have one eye a bit stronger than the other.
Optical Coatings and Light Transmission
 Objective Lenses of a Binocular
Objective Lenses of a BinocularOne of the most important and expensive elements in a binocular is the optical coating of the lenses in a binocular. This applies to any optical device, for that matter. As light hits a lens, some of it gets lost in the optic and does not transmit further. To achieve greater light transmission, optics are coated with special chemicals. The goal of any optic is to maximize the amount of light entering the objective lens to the eye.
Binoculars are designated as coated, fully coated, multi-coated, or fully multi-coated. This tells you how many layers of optical coatings are on how many lens surfaces.
- Coated Lenses - a single layer on at least one lens surface.
- Fully Coated Lenses - a single layer on all air-to-glass surfaces.
- Multi-Coated Lenses - multiple layers on at least one lens surface.
- Fully Multi-Coated - multiple layers on all air-to-glass surfaces.
With fully multi-coated lenses it is possible to achieve close to 95% light transmission. That means that 95% of all light coming through the objective lens reaches the eye. The image is of higher contrast and appears more clearly than with fewer lens coatings. Better optical quality also delivers better resolution, or the ability to distinguish between fine details and retain clarity.
Binocular Tips
- Binoculars Weight - Most people find that anything more than 35 ounces is too much to comfortably carry around the neck and a weight of fewer than 30 ounces is much better. If your current binocular is becoming a pain in the neck, you might want to look at a binocular harness, which supports the weight on your shoulders rather than your neck.
- Binocular Tripod Mounting - Any time you have a binocular magnification over 10x or 12x and other high-power binoculars you should attach a binocular to a tripod to steady the image. Also, heavy binoculars with the last number of 70mm or more usually need a tripod to support the weight. You can mount a binocular to a tripod if it is listed as tripod adaptable or if it is threaded for a tripod adapter. If it is listed as tripod adaptable, you will still need to purchase a tripod adapter, though a few large binoculars have this accessory built-in.
- Cleaning the Lenses - When cleaning the binocular lens surface, use a microfiber cloth that is usually included with the binocular unit in a circular motion to protect the coatings on the lenses. Do not use a finger or sharp objects to clean the lenses to avoid scratches and removing the chemical layers.
Having the right binocular accessories like a cleaning cloth or bino harness ensures that your optic will perform at its best for years to come.
You can also check out our binocular reviews from other customers to see what they have to say!













