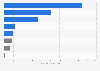
Share of electricity production FY 2023, by energy source
In the fiscal year 2023, around 33 percent of electricity in Japan was generated from natural gas. Renewable energy accounted for almost 23 percent of the electricity generation in the country, reaching a peak in the last decade.
Electricity market in Japan
In recent years, the Japanese electricity market was dominated by ten regional electricity companies. Competition remained limited since retailers of low voltage electricity mainly sell their product locally to homes and small shops.
The nuclear disaster in 2011 influenced the electricity market insofar that nuclear energy was replaced by fossil fuels such as natural gas and coal. Since Japan lacks domestic reserves of fossil fuels, it is heavily dependent on imports. This caused a decline in the self-sufficiency rate of primary energy, and an increase in electricity rates for homes shortly after the disaster.
Current energy policy in Japan
To be more independent of fossil fuel imports as well as to reduce its carbon footprint and electric power costs, Japan currently aims to replace fossil fuels with low carbon energies such as nuclear and renewable energy sources. To realize its climate goals, the Japanese government plans to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by 46 percent, compared to the level of 2013, until 2030. Furthermore, it announced its intention for the country to be entirely emission-free by 2050.
In recent years, the share of renewable energy in electricity production increased significantly, with solar and hydropower representing the largest renewable energy sources. Nevertheless, there was international criticism that Japan is unlikely to expand its renewable energy share sufficiently to achieve its climate goals for 2050.