Share of world population living in poverty 1990-2022
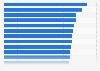
Over the past 30 years, there has been an almost constant reduction in the poverty rate worldwide. Whereas nearly 38 percent of the world's population lived on less than 2.15 U.S. dollars in terms of 2017 Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) in 1990, this had fallen to 8.7 percent in 2022. This is despite the fact that the world's population was growing over the same period. However, there was a small increase in the poverty rate during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021, when thousands of people became unemployed overnight. Moreover, rising cost of living in the aftermath of the pandemic and spurred by the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022 meant that many people were struggling to make ends meet.
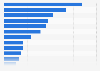
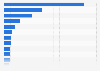
Poverty is a regional problem
Poverty can be measured in relative and absolute terms. Absolute poverty concerns basic human needs such as food, clothing, shelter, and clean drinking water, whereas relative poverty looks at whether people in different countries can afford a certain living standard. Most countries that have a high percentage of their population living in absolute poverty, meaning that they are poor compared to international standards, are regionally concentrated. African countries are most represented among the countries in which poverty prevails the most. In terms of numbers, Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia have the most people living in poverty worldwide.
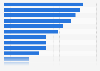
Inequality on the rise
How wealth, or the lack thereof, is distributed within the global population and even within countries is very unequal. In 2022, the richest one percent of the world owned almost half of the global wealth, while the poorest 50 percent owned less than two percent in the same year. Within regions, Latin America had the most unequal distribution of wealth but this phenomenon is present in all world regions.